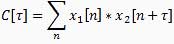Time Delay Estimation
A signal emanating from a remote source and monitored in the presence of noise at two spatially separated sensors is modeled as:
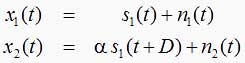
Using Generalized Cross Correlation we can find the delay between each sensor. The techniques for this vary although the general idea remains the same. A pre-filter specific to the method, is used in the frequency domain to 'clean up' the signal. It then undergoes cross correlation and a peak detection on that result to determine the point of maximum delay. The image below shows the continuous time model for the application of Generalized Cross Correlation(GCC). In this model, the use weighting functions, or pre-filters is utilized to 'clean' the signal into a more useful form. For the purposes of this experiment, the methods used were the standard cross correlation, PHAT, and SCOT methods.
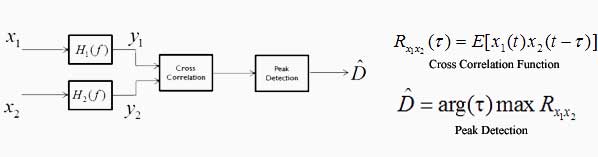
The methods above are in continuous time while the experiment is based in a digital system that uses discrete time. The overall aspects of application are rooted in the same concepts except that the cross correlation function is replaced by its discrete time counter part shown below. In application, the actual calculations were performed by MATLAB.